observed optical rotation polarimeter|what does a polarimeter measure : importer Is there a maximum optical rotation of plane polarized light that can be observed using a polarimeter? I understand that in a polarimeter, light . 29 de nov. de 2023 · Link: https://thunderstore.io/c/lethal-company/?ordering=most-downloadedQuiero agradecer a mi amigo Zerrotgus por mostrarme y enseñarme esta manera de instal.
{plog:ftitle_list}
WEBO dia 5 de cada mês é o [Dia do Membro] do FB.bet, mais de R$ 10 milhões em bônus serão distribuídos naquele dia! O FB.bet também distribuirá bônus misteriosos de vez em quando em outros momentos, então fique ligado! 6. Se houver uma perda de mais de 5R$ no dia, você também pode participar do recebimento de um fundo de resgate de FB .
why polarimeter is used
Generally, the observed optical rotation at 436nm is approximately double and at 365nm about three times that at 589nm. Polarimeter Light Sources. It is now common practice to use other light sources such as xenon or tungsten halogen.
which lamp used in polarimeter
The observed rotation of the mixture is levorotary (negative, counter-clockwise), and the specific rotation of the pure enantiomer is given as dextrorotary (positive, clockwise), meaning that the . Is there a maximum optical rotation of plane polarized light that can be observed using a polarimeter? I understand that in a polarimeter, light .
Before we begin, it's very important to distinguish two types of optical rotation. The first is the real optical rotation, $\alpha_{real}$. This is the twist which a substance actually causes on the plane of polarized light as it . The plane of polarization can be determined by an instrument called a polarimeter, shown in . The optical rotation of a neat sample of a mixture of R and S carvone is measured at (-)23°. Which enantiomer is in excess, and what is its ee? What are the percentages of (R)- and (S)-carvone in the sample? Solution. The observed rotation of the .It is the optical rotation for a given concentration, sample cell length, temperature, and wavelength. In turn, if you know the substance’s specific rotation, the concentration can be determined from the optical rotation .
where α is the observed rotation, l is the path length of the cell (measured in decimetres, dm), . Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\): Operating principle of an optical polarimeter. 1. Light source 2. Unpolarized light 3. Linear polarizer 4. Linearly polarized light 5. Sample tube containing molecules under study 6. Optical rotation due to molecules 7.
Specific Rotation— The reference Specific rotation 781S in a monograph signifies that specific rotation is to be calculated from observed optical rotations in the Test solution obtained as directed therein. Unless otherwise directed, measurements of optical rotation are made at 589 nm at 25.Where a photoelectric polarimeter is used, a single measurement, corrected for the . Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\): The effect of path length on optical rotation. The longer the path of light through a solution of molecules, the more molecules will be encountered by the light, and the greater the optical rotation. The value of the optical rotation must be corrected for the length of the cell used to hold the sample.
what does a polarimeter measure
schematic diagram of polarimeter
compression test snow
Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\): The effect of path length on optical rotation. The longer the path of light through a solution of molecules, the more molecules will be encountered by the light, and the greater the optical rotation. The value of the optical rotation must be corrected for the length of the cell used to hold the sample.
A polarimeter [1] is a scientific instrument used to measure optical rotation: the angle of rotation caused by passing linearly polarized light through an optically active substance. [ 2 ] Some chemical substances are optically active, and linearly polarized (uni-directional) light will rotate either to the left (counter-clockwise) or right .
Optical rotation The optical rotation is the angle through which the plane of polarization is rotated when polarized light passes through a layer of a . where a is the observed rotation, l is the length of the observed layer in mm, c is the number of g of substance contained in 100 . Optical rotation is measured with a polarimeter. The zero . Specific Optical Rotation Optical rotation is determined using a polarimeters The general equation for Specific Optical Rotation; [α] = specific rotation at wavelength λ T = temperature # a = Observed rotation in degrees (°) l = path length (dm) C = concentration of the analyte (g/100 mL) D-line of the sodium lamp at the visible wavelength .
Place the cell in the polarimeter and adjust the polarimeter until the reading stabilizes. Record the reading and repeat the process with the same sample to ensure accuracy. Calculate the specific rotation value using the formula: Specific Rotation = Observed Rotation / (Concentration × Cell Length) Where: Determine the zero point of the polarimeter and then make five readings of the observed rotation of the test solution at 25°. Take an equal number of readings in the same tube with the solvent in place of the test solution. The zero correction is the average of the blank readings, and is subtracted from the average observed rotation if the two figures are of the .
The Lippich polarimeter is a more accurate variant. An improved method, based on an intervention of the Austrian physicist Ferdinand Franz Lippich in the late 19 th century, uses an additional optical element which introduces some rotation of the polarization direction for about half of the beam area after the polarizer. One can then not obtain .The value of the optical rotation must be corrected for the length of the cell used to hold the sample. In summary: \[[\alpha] = \frac{\alpha}{c \times l} \nonumber\] a is the measured optical rotation. c is the sample concentration in grams per deciliter (1 dL = 10 mL). That is, c = m / V (m = mass in g, V = volume in dL). l is the cell length .The degree of rotation observed in a polarimeter, α, is dependent on the number of chiral species the light encounters on its passage through the sample chamber, as well as the wavelength of the light. Thus, analytical accuracy dictates strict control of a number of experimental parameters, such as temperature, concentration, light source, and .
where α obs is the observed optical rotation value given by the polarimeter, l is the cell pathlength in dm, and c is the concentration of the solution in g/mL. Moreover, the enantiomeric excess ( ee ), which is a measurement of how much of one enantiomer exists over the other in a mixture, can be determined by using specific rotation.Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\): Operating principle of an optical polarimeter. 1. Light source 2. Unpolarized light 3. Linear polarizer 4. Linearly polarized light 5. Sample tube containing molecules under study 6. Optical rotation due to molecules .The influence of polarimeter design on the observed signal-to-noise characteristics has been discussed by a number of investigators. . A reasonable criterion for acceptability is that the observed optical rotation should be within ±0.5% of the certified value. The quartz plates are available from a variety of sources, including manufacturers .
The rotation degree measured by the polarimeter is called the observed rotation . To compare the optical rotation between different compounds under consistent conditions, the specific rotation is used. Specific rotation is the rotation caused by a solution with concentration of 1.0 g/mL in a sample tube of 1.0 dm length. The temperature is .A polarimeter is a device that measures the rotation of linearly polarized light by an optically active sample. This is of interest to organic chemists because it enables differentiation between optically active stereoisomers, i.e., enantiomers. . where α is the observed optical rotation in units of degrees, [α] is the specific rotation in .The rotation degree measured by the polarimeter is called the observed rotation (α), and the observed rotation depends on the length of the sample tube, the concentration of the sample and the temperature. To compare the optical rotation between different compounds under consistent conditions, the specific rotation is used.
According to Biot’s Law, the observed optical rotation ⍺ depends on the path length through which light must pass through the sample. In this experiment, students will observe how observed optical rotation and path length are related. . Pour the Mexican Sprite into the polarimeter and measure its optical rotation. Use the calibration .
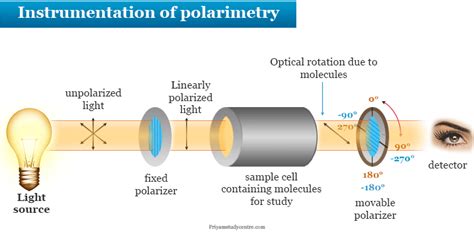
The optical rotation is measured through a polarimeter. The optical activity of optically active substances is studied by the polarimeter. Polarimetry Gives the measurement of rotation of plane-polarized light by an optically active substance. . Optical rotation can be observed when any type of substance is used as the sample while Specific .
traditional polarimeter is the use of a Polaroid sheet in the optics instead of the very expensive crystal prisms. This material was developed by E. H. Land, the founder of Polaroid Corporation. The Qualitative Use of the Polarimeter. Once you have a polarimeter available, the phenomenon of optical rotation is quite easy to demonstrate.Optical Rotation with a Novel Polarimeter . their optical axes will become parallel at the rotational angle of the analyser Ao at which the illumination output observed by the photo-detector and recorded by its supporting circuitry reaches its maximum value. If the analyzer is then rotated to the angular position A, as illustrated in Figure 1 .
The influence of polarimeter design on the observed signal-to-noise characteristics has been discussed by a number of investigators. . A reasonable criterion for acceptability is that the observed optical rotation should be within ±0.5% of the certified value. The quartz plates are available from a variety of sources, including manufacturers .10. What is the specific optical rotation of (S)-malic acid at a concentration of 5.5 g/ mL in the solvent pyridine at 20°C at a wavelength of 589 nm? a) the specific rotation is –27° b) the specific rotation is +27° c) the specific rotation is –17° d) the specific rotation is +17° View Answer
optical rotation vs specific
how to calculate optical rotation
Nadson o Ferinha. Cifra: Principal (violão e guitarra) Favoritar Cifra. Tom: G#m. [Intro] G#m7 B2 C#m7 E9 G#m7 Sabe quando a gente termina B2 Um relacionamento C#m7 .
observed optical rotation polarimeter|what does a polarimeter measure